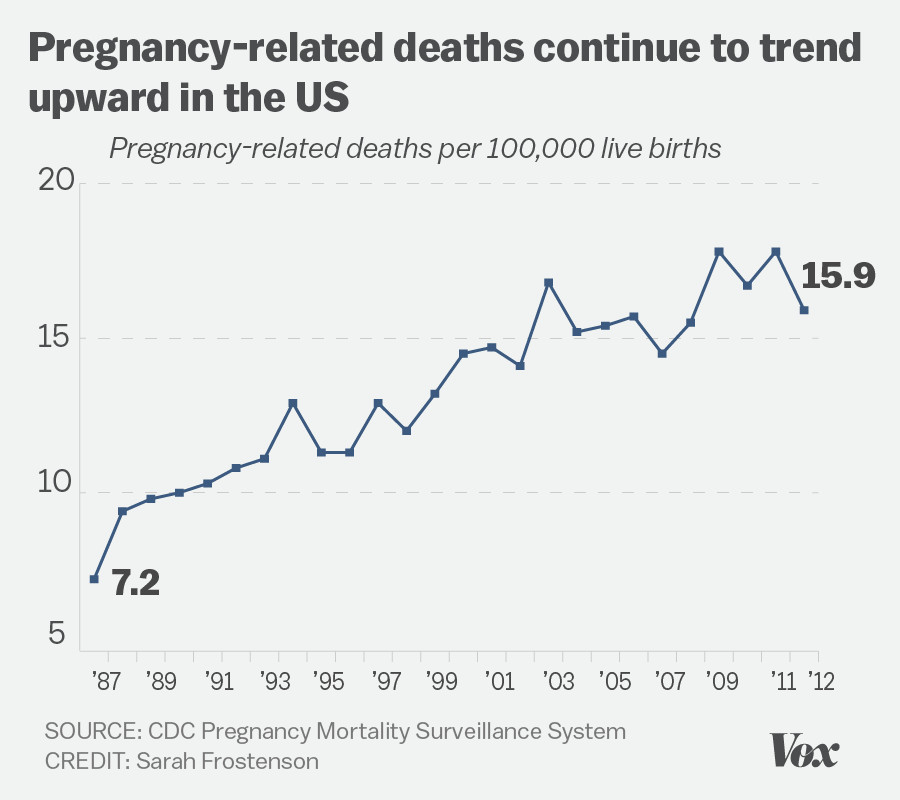
In recent years, U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have garnered increasing attention as alarming rates continue to escalate, making the nation the leader in maternal mortality among high-income countries. A significant portion of these deaths, over 80%, is preventable, highlighting the urgent need for improved pregnancy care and better access to critical postpartum health services. Between 2018 and 2022, the maternal mortality rate saw a troubling rise, exacerbated by chronic conditions in pregnancy and stark racial disparities in maternal health. The findings emphasize the necessity of addressing systemic issues within the healthcare system, including examining the impact of inequitable policies and biases affecting minority groups. As we delve deeper into this pressing issue, it’s clear that a comprehensive overhaul of how we approach maternal health is imperative for saving lives and ensuring safer pregnancies across all demographics.
The topic of maternity health has become increasingly relevant as the U.S. faces a crisis in preventing pregnancy-related fatalities. This issue, often referred to as maternal mortality, encompasses the various complications and health risks associated with childbirth and the postpartum period. With the persistent increase in fatalities, especially among marginalized groups, it is crucial to investigate the systemic barriers within our healthcare system, including maternity care deserts and the influence of chronic conditions in pregnancy. Furthermore, addressing the growing racial disparities in maternal health outcomes requires a concerted effort to reshuffle health policies and care models. By tackling these issues, we can pave the way for a more equitable and effective approach to maternal care, ultimately reducing the number of preventable deaths.
Understanding U.S. Pregnancy-Related Deaths: A Growing Crisis
The issue of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths has emerged as a concerning crisis, with a significant portion of these deaths being preventable. Unfortunately, the U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, an alarming statistic that underscores systemic flaws within the healthcare framework. Between 2018 and 2022, research indicates an ongoing rise in these rates, prompting urgent calls for improved pregnancy care and postpartum support. Many fatalities could be mitigated with enhanced healthcare strategies, making it imperative to address the root causes of these deaths to save lives.
Data highlights stark racial and ethnic disparities in maternal mortality rates, with American Indian and Alaska Native women disproportionately affected. The disparity reflects broader societal issues such as access to quality healthcare and responses to chronic conditions in pregnancy. Therefore, addressing U.S. pregnancy-related deaths not only requires improvements in medical care but also a commitment to tackling systemic inequalities that lead to divergent health outcomes. Expanding healthcare access and support can play a crucial role in reversing this troubling trend.
The Role of Maternal Mortality Rate in Pregnancy Health
Examining the maternal mortality rate reveals critical insights into pregnancy health across different demographics. This rate is a key indicator of the overall health of a nation’s population and its healthcare effectiveness. The continued rise in U.S. maternal mortality rates, in stark contrast to countries with better outcomes, highlights the urgent need for systemic reform. Each state demonstrates varied mortality figures, reflecting disparate access to care that can result in significant outcomes. Understanding this data is essential for healthcare policymakers seeking to reverse these trends.
Enhancing the maternal mortality rate means addressing factors such as chronic conditions and access to prenatal care services. Innovations in pregnancy care must incorporate strategies to better manage chronic diseases that disproportionately affect certain populations. The stark realities of pregnancy-related deaths drive home the necessity of a nuanced approach that aims for more equitable health outcomes. By focusing on these advancements, the long-term goal of reducing the maternal mortality rate can be achieved.
Racial Disparities in Maternal Health: An Ongoing Challenge
Racial disparities in maternal health persist as a critical issue within the United States, where the data shows significant variations in pregnancy-related mortality based on race. A shocking statistic is that American Indian and Alaska Native women have a maternal mortality rate nearly four times higher than that of white women. These disparities not only reflect access to healthcare but also broader societal inequities and chronic health conditions that disproportionately affect racial minorities. Faced with this challenge, there is an urgent need for tailored interventions that specifically address the unique barriers encountered by these communities.
Addressing racial disparities in maternal health encompasses the need for culturally competent care and community-based health interventions. Efforts must focus on breaking down systemic barriers that contribute to these inequalities, including access to prenatal and postpartum care. Improving education and resources within marginalized communities can empower individuals and healthcare providers to work together toward safer pregnancy outcomes. Targeted strategies are crucial to ensure that the maternal health crisis does not perpetuate cycles of inequity in the United States.
The Impact of Chronic Conditions in Pregnancy
Chronic conditions during pregnancy represent a critical factor in the growing rates of maternal mortality. For instance, the prevalence of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases has increased among younger women, reflecting alarming trends that necessitate urgent attention. The shift from hemorrhage as the leading cause of pregnancy-related death to cardiovascular complications emphasizes the need for improved awareness and management of these conditions. Recognizing and addressing chronic conditions early is essential for enhancing maternal health and reducing preventable deaths.
Furthermore, effective pregnancy care should incorporate routine screenings for chronic health issues and integrate treatment strategies throughout the pregnancy continuum. Health practitioners must prioritize early interventions and create personalized care plans that account for existing chronic conditions. By doing so, the healthcare system can better support expectant mothers, ultimately decreasing the risks associated with chronic diseases in pregnancy and fostering healthier outcomes.
Extended Postpartum Health: An Overlooked Aspect of Maternal Care
The postpartum period is traditionally designated as the six-week recovery phase following childbirth; however, this perspective neglects the complexities of maternal health beyond that time frame. Recent findings indicate that nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur post the immediate postpartum period—up to one year later. This alarming statistic illuminates the necessity for an expanded definition of postpartum care that includes ongoing support for mothers. By reevaluating healthcare post-birth, maternal health policies can effectively respond to potential dangers that arise beyond the initial recovery phase.
Supporting postpartum health requires an integrated approach that provides resources and continuous medical support to mothers as they transition into new parenting roles. Many women face physical and emotional challenges during the postpartum year that far exceed the six-week standard. Incorporating education and comprehensive care during this extended period can empower mothers to recognize warning signs and seek necessary medical attention. Addressing postpartum health in a broader context can reduce the incidence of late maternal deaths and shape better overall health strategies.
Pregnancy Care Policies: Bridging the Gap in Maternal Health
The landscape of pregnancy care policies across the United States presents a patchwork of regulations that can greatly affect outcomes for mothers and their babies. Inequities in care access, especially across different states, result in varying maternal mortality rates which threaten public health efforts. California serves as an example where improved policies and practices have led to significant reductions in pregnancy-related deaths. This indicates that there is a need for comprehensive policy reforms aimed at standardizing quality pregnancy care nationwide.
Investing in evidence-based pregnancy care policies can bridge the gap in maternal health outcomes and ensure that every woman receives quality support throughout her reproductive journey. Policymakers must focus on implementing programs that enhance prenatal care, postpartum support, and address chronic health conditions among pregnant individuals. With targeted investments and political will, it is possible to cultivate a healthcare environment where maternal mortality rates decline, and every pregnancy experience is safe and supported.
Innovations in Maternal Health Solutions: A Path Forward
As the statistics around U.S. pregnancy-related deaths continue to rise, innovative solutions in maternal health may offer pathways to effectively reduce these figures. Research and technological advancements enable providers to better monitor and manage potential risks associated with pregnancy. From remote patient monitoring to telehealth consultations, healthcare systems now have access to tools that can improve pregnancy outcomes. These innovations are essential for addressing the chronic conditions that often contribute to pregnancy complications and fatalities.
Moreover, leveraging community-based initiatives to educate and empower mothers on self-advocacy can enhance their health during pregnancy. By fostering partnerships between healthcare professionals and communities, there is a greater potential for developing tailored interventions that enhance maternity care. Investments in these progressive solutions align with the goal of reducing maternal mortality rates and ensuring comprehensive care throughout prenatal and postpartum periods.
The Importance of Tracking Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Accurate tracking of pregnancy-related deaths is crucial in understanding and addressing the maternal mortality crisis. Until recently, the lack of a standardized national system has hindered efforts to assess and respond to these deaths effectively. Since the implementation of specific measures in 2018, researchers have gained greater insights into the nature of these fatalities, enabling a stronger response to the urgent needs. Consistent tracking of deaths can inform healthcare policies and help pinpoint critical intervention areas.
Establishing a reliable framework for monitoring maternal deaths not only enhances data collection but also highlights crucial patterns related to race, socioeconomic status, and healthcare disparities. By investing in robust monitoring systems, stakeholders can develop targeted strategies to mitigate preventable deaths. Ultimately, understanding the underlying factors contributing to maternal mortality will guide efforts to create a safer pregnancy landscape within the United States.
Advocacy and Community Engagement in Maternal Health
Advocacy plays a vital role in addressing the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths. Grassroots movements and community organizations are increasingly active in raising awareness and promoting policy changes that prioritize maternal health. These efforts often lead to a greater understanding of the disparities faced by different racial and ethnic groups, prompting local and federal initiatives to enhance pregnancy care access. Engaging with communities serves not only to educate but also to empower individuals in seeking better healthcare options.
Furthermore, community engagement fosters collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and advocates to enact meaningful change. Open dialogue about pregnancy experiences and health outcomes can shine a light on the critical aspects of maternal health that need immediate attention. By fostering a more informed public and creating strong advocacy networks, there’s a greater potential to influence healthcare policies that will lead to improved quality of care and reduce the risk of maternal mortality across diverse populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the current statistics on U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
As of 2022, the maternal mortality rate in the U.S. stands at 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births, marking an increase from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018. This alarming statistic highlights the continuing rise of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., particularly during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
How do chronic conditions in pregnancy contribute to pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular diseases significantly increase the risk of pregnancy-related deaths. Recent studies indicate a troubling rise in these chronic health issues among younger individuals, contributing heavily to the mortality rate during and after pregnancy.
Why are there racial disparities in maternal health and pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Racial disparities in maternal health and pregnancy-related deaths can be attributed to factors such as systemic bias, inequitable healthcare policies, and socioeconomic disparities. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience mortality rates nearly four times higher than white women, highlighting significant inequities in pregnancy care across racial groups.
What is the importance of extended postpartum health in the context of U.S. pregnancy-related deaths?
Extended postpartum health is crucial because nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and 1 year after pregnancy. Recognizing this period as part of maternal health can lead to better healthcare strategies aimed at preventing late maternal deaths and ensuring comprehensive care beyond the traditional postpartum window.
How can the U.S. improve its maternal mortality rate compared to other high-income countries?
To improve its maternal mortality rate, the U.S. must enhance its healthcare system by implementing equitable policies, ensuring better access to pregnancy care, and addressing chronic health conditions more effectively. Data shows that states like California have successfully reduced pregnancy-related deaths, serving as a model for national improvement.
What are the leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The leading cause of pregnancy-related death in the U.S. is cardiovascular disease, which accounts for over 20% of such deaths. This shift from hemorrhage to cardiovascular issues underscores the growing prevalence of chronic health conditions impacting maternal health.
Why is the tracking of pregnancy-related deaths important for improving maternal health outcomes?
Tracking pregnancy-related deaths is vital as it provides crucial data on maternal health trends, allowing policymakers and healthcare providers to understand and address the causes effectively. The implementation of uniform death certificate protocols in 2018 has significantly improved the accuracy of mortality data, highlighting the areas that need urgent attention.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Rates | U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, continuing to rise from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women have the highest mortality rate at 106.3, while white women’s rate is 27.6. |
| Healthcare System Issues | Factors include a patchwork healthcare system, inequitable policies, and health care deserts. |
| Cardiovascular Disease | Over 20% of deaths are due to cardiovascular issues, which are increasingly affecting younger individuals. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year post-pregnancy) account for nearly a third of total deaths. |
| Need for Better Care | More investment is needed in public health and postpartum care systems to reduce mortality rates. |
| Tracking Improvements | Implementation of pregnancy checkboxes on death certificates since 2018 has improved tracking of maternal deaths. |
Summary
U.S. pregnancy-related deaths have become a critical issue, as the maternal mortality rate continues to escalate, highlighting the urgent need for systemic healthcare reforms. With over 80% of these deaths deemed preventable, the focus must shift toward enhancing prenatal care and addressing disparities in health outcomes across racial and ethnic groups. Increased investment in public health infrastructure, particularly in postpartum care, is vital to mitigate this crisis, ensuring that more mothers can receive comprehensive healthcare and support throughout their pregnancy journey.