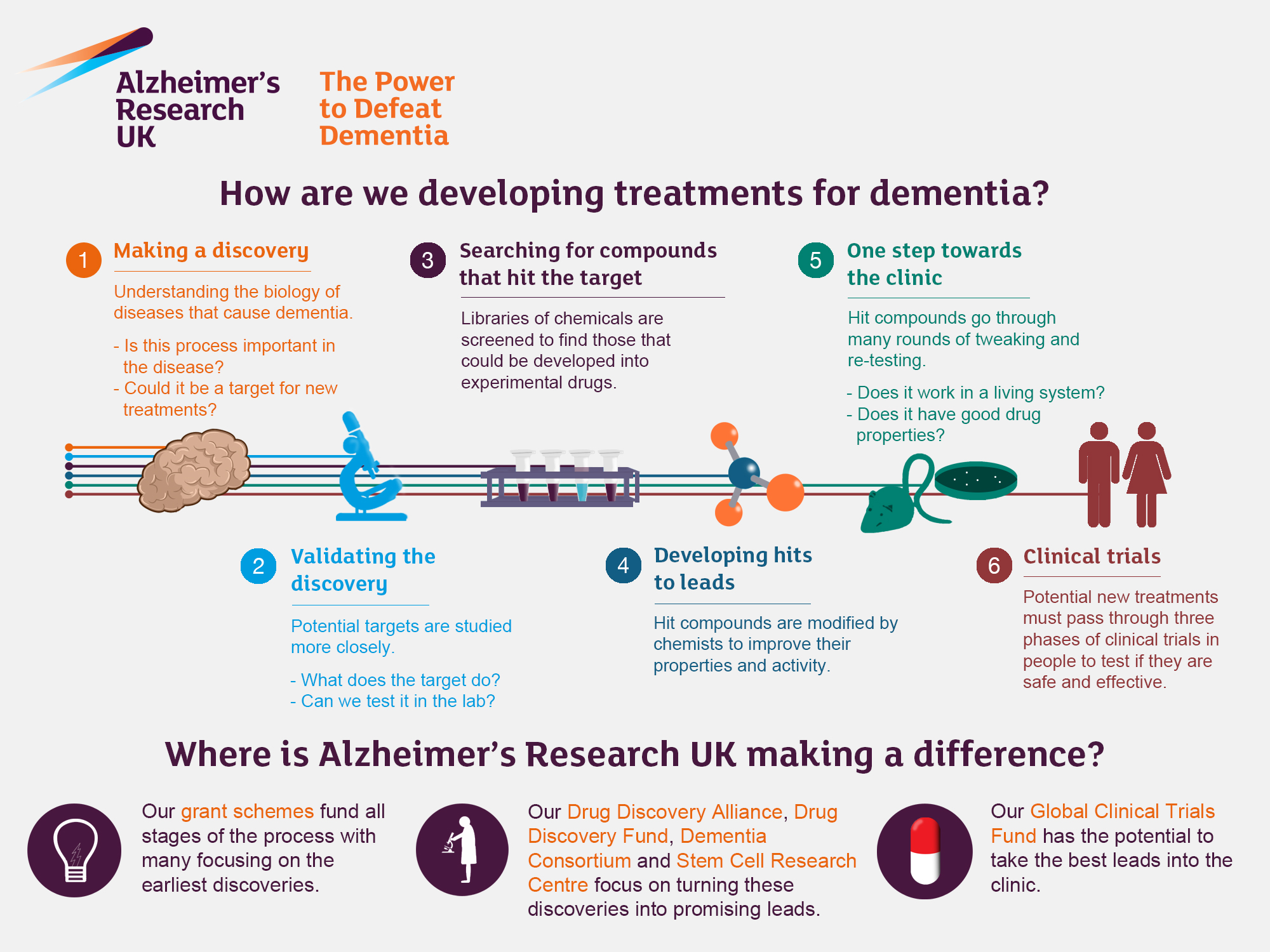
Alzheimer’s research is at the forefront of understanding and combating neurodegenerative diseases that affect millions worldwide. Led by pioneering scientists like Beth Stevens, this field explores the critical role of microglial cells—often referred to as the brain’s immune system—in maintaining neurological health. These cells play a vital part in clearing damaged neurons and pruning excess synapses; however, irregularities in their function can contribute to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease and other memory-related disorders. With an aging population, the urgency for effective Alzheimer’s treatments is more critical than ever, as the number of affected individuals continues to rise dramatically. Discoveries rooted in these groundbreaking studies are paving the way for innovative therapeutic approaches and earlier detection methods, potentially revolutionizing care for those living with Alzheimer’s.
The investigation into Alzheimer’s disease encompasses a broad spectrum of scientific inquiry surrounding cognitive decline and memory loss. Neurological research is increasingly focusing on how the immune processes in the brain, particularly through the action of microglial cells, can influence the trajectory of diseases like Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s. Cutting-edge work by researchers, including notable figures such as Beth Stevens, emphasizes the potential of these immune cells in shaping synaptic connections and their irregularities leading to neurodegenerative disorders. As scientists delve deeper into this complex interplay, new pathways for Alzheimer’s treatment emerge, highlighting the importance of foundational research in understanding and addressing the growing challenge of dementia-related illnesses.
The Role of Microglial Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease
Microglial cells serve as the brain’s immune system, playing a crucial role in maintaining neuronal health and homeostasis. They are responsible for monitoring and responding to changes in the central nervous system (CNS), which includes clearing away cellular debris and modulating synaptic connections. In Alzheimer’s disease, the functionality of microglial cells can become compromised, leading to ineffective pruning and clearing of synapses, potentially accelerating cognitive decline. Beth Stevens’ groundbreaking research highlights the dual role of these cells, illustrating how they contribute to both the health and pathology of the brain.
Aberrant microglial activity has been linked to various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s disease. Stevens’ studies underscore the importance of understanding microglial behavior, as their failure to effectively manage synaptic connections can result in the accumulation of toxic proteins associated with Alzheimer’s. This critical insight provides a pathway for the development of targeted Alzheimer’s treatments that aim to restore proper microglial function, offering hope for millions affected by this devastating illness.
Alzheimer’s Research: Paving the Way for New Treatments
The ongoing research at Beth Stevens’ lab exemplifies how fundamental science can lead to innovative treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. By focusing on the mechanisms through which microglial cells operate, the lab has identified potential biomarkers that could help in early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s. Understanding the intricate relationship between these immune cells and neurodegenerative processes allows for the identification of therapeutic targets that could modify disease progression and improve patient outcomes.
Moreover, Stevens emphasizes the necessity of federal support in advancing Alzheimer’s research. The backing received from institutes like the National Institutes of Health has not only propelled investigation into microglial dynamics but has also facilitated a deeper understanding of their implications in Alzheimer’s and other related disorders. With the anticipated growth of Alzheimer’s diagnoses in coming decades, researchers like Stevens stand at the forefront of developing strategies to combat this escalating health crisis.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research
As the landscape of Alzheimer’s research continues to evolve, the contributions from pioneering scientists like Beth Stevens are vital. Future endeavors will likely delve deeper into the complexities of microglial behavior and its influence on neurodegeneration. By integrating advanced technologies and interdisciplinary approaches, researchers can uncover novel therapeutic avenues that may lead to effective treatments for Alzheimer’s patients. The aim is to shift the focus from solely managing symptoms to altering the course of the disease itself.
Furthermore, the importance of collaboration and funding in Alzheimer’s research cannot be overstated. Support from governmental health agencies, private foundations, and academic institutions is critical for nurturing innovative ideas and translating them into real-world applications. As the scientific community rallies to better understand Alzheimer’s disease, the hope is that new findings will translate into meaningful interventions that enhance the quality of life for those affected by this and other neurodegenerative conditions.
The Impact of Neurodegenerative Diseases on Society
Neurodegenerative diseases, especially Alzheimer’s, pose a growing threat to global health, particularly as populations age. With projections indicating a doubling in the number of Alzheimer’s cases by 2050, society faces not only a medical challenge but also an economic one. The financial burden associated with the care of Alzheimer’s patients is staggering, with estimates suggesting costs could soar from $360 million to $1 trillion. Addressing this crisis requires a concerted effort to advance research, improve caregiving options, and bolster support for affected families.
Public awareness and education about Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases are essential to foster understanding and compassion towards individuals and families impacted by these conditions. Additionally, initiatives aimed at early detection and intervention can play a crucial role in alleviating some of the societal pressures related to these diseases. As researchers like Beth Stevens continue to explore the biological underpinnings of Alzheimer’s, society must also advocate for robust support systems that empower both patients and caregivers.
Understanding the Brain’s Immune System
The brain’s immune system, largely mediated by microglial cells, is foundational to understanding neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. These cells are not only defenders of the CNS but also activators of various neuroinflammatory responses that can influence disease outcomes. Research focused on how microglial cells respond to pathological states is critical for developing therapeutic strategies. Understanding their role in pruning and synaptic health can provide insights into the degeneration process seen in Alzheimer’s patients.
As neuroscience continues to unveil the complexities of the brain’s immune response, it becomes increasingly evident how interconnected these systems are with neurodegenerative diseases. Advancements in this area could lead to new strategies that bolster microglial function, potentially mitigating the impacts of Alzheimer’s. By targeting the brain’s immune system, researchers aim to not only halt disease progression but also enhance cognitive resilience in older populations.
Discoveries in Basic Science and Their Relevance
The importance of basic science in neuroscience cannot be underestimated, especially in its applications to diseases like Alzheimer’s. Basic research provides the groundwork that informs our understanding of complex biological interactions within the brain. Stevens’ lab exemplifies the power of curiosity-driven exploration, leading to breakthroughs that challenge existing paradigms about microglial cells and their role in synaptic pruning. These discoveries pave the way for potential therapeutic interventions that target fundamental processes within the brain.
Moreover, the translation of findings from basic science into clinical applications is a critical component of effective Alzheimer’s research. Understanding the implications of microglial function in disease pathology is a stepping stone towards developing innovative treatments. As such, fostering environments that prioritize basic research will be essential for discovering new pathways for intervention that can ultimately improve outcomes for Alzheimer’s patients.
The Significance of Federal Funding in Alzheimer’s Research
Federal funding plays a pivotal role in advancing Alzheimer’s research, as highlighted by Beth Stevens’ experience. The support from the National Institutes of Health and similar organizations allows researchers to pursue innovative lines of inquiry that might otherwise be overlooked. This funding not only propels research efforts but also facilitates collaboration among scientists striving to expand knowledge on neurodegenerative diseases. The sustained investment in such research indicates a commitment to combating the Alzheimer’s epidemic.
Additionally, federal grants can help bridge the gap between preliminary findings and clinical applications. The pursuit of knowledge in understanding complex diseases like Alzheimer’s requires substantial resources, and federal support provides a crucial lifeline for researchers navigating this challenging landscape. By recognizing the value of funding in driving scientific progress, society can ensure that critical research continues and that effective treatment options emerge for those afflicted with Alzheimer’s.
Promising Developments in Alzheimer’s Treatment
Recent advancements in Alzheimer’s treatment research reflect a growing understanding of the disease’s underlying mechanisms. Treatments targeting the immune response within the brain are becoming more prominent, as researchers seek to enhance the natural capabilities of microglial cells. By developing drugs aimed at correcting aberrant pruning and promoting proper synaptic function, the path to manageable Alzheimer’s treatment appears more feasible than ever. The potential for these treatments highlights the importance of foundational research in informing clinical applications.
Moreover, the incorporation of biomarker discovery is a game changer in the treatment landscape. Early detection via biomarkers can revolutionize how Alzheimer’s is managed, shifting the focus towards preventive care rather than purely reactive measures. As research progresses, the culmination of innovative therapies and early detection methods presents a holistic approach to diminishing the impact of Alzheimer’s disease on individuals and society as a whole. The future of Alzheimer’s treatment is bright, fueled by ongoing discoveries in microglial research.
Advocating for Alzheimer’s Awareness and Support
Raising awareness about Alzheimer’s disease is essential in fostering societal understanding and support for affected individuals and families. Advocacy efforts aim to illuminate the challenges associated with the disease, emphasizing the need for increased funding for research and improved caregiver resources. By engaging the public in conversations surrounding Alzheimer’s, we cultivate empathy and inspire action that can lead to meaningful changes within healthcare systems.
Furthermore, creating robust support networks for caregivers and patients can help alleviate some of the emotional and financial burdens associated with Alzheimer’s. Communities can mobilize to provide resources, training, and respite for families, ensuring they are equipped to handle the complexities of caregiving. With researchers like Beth Stevens leading the charge on scientific discovery, the combination of awareness and support will be instrumental in addressing the multifaceted challenges posed by Alzheimer’s disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do microglial cells play in Alzheimer’s research?
Microglial cells are essential components of the brain’s immune system and play a critical role in Alzheimer’s research. They help maintain brain health by clearing out dead cells and pruning synapses. However, aberrant microglial activity can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, making them a focal point for researchers aiming to develop effective treatments.
How does Beth Stevens contribute to Alzheimer’s treatment through her research?
Beth Stevens has significantly advanced Alzheimer’s treatment by investigating microglial cells and their impact on synaptic pruning. Her research highlights how improper pruning can lead to neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, and paves the way for new therapeutic strategies and early detection biomarkers, ultimately improving care for millions affected by the disease.
What is the significance of the brain immune system in Alzheimer’s disease?
The brain’s immune system, primarily represented by microglial cells, is crucial in Alzheimer’s disease research. These cells protect the brain by removing damaged cells and modulating inflammation. Understanding their dysfunction provides insights into the mechanisms of Alzheimer’s, offering potential targets for innovative treatments and interventions.
What are the implications of Beth Stevens’ findings on neurodegenerative diseases?
Beth Stevens’ findings reveal that dysfunctional microglial activity can escalate conditions like Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s diseases. Her research underscores the importance of addressing neuroinflammation and synaptic pruning in developing new treatments and improves our ability to diagnose and intervene in neurodegenerative diseases at earlier stages.
How does researchers’ understanding of microglial cells influence Alzheimer’s drug development?
The evolving understanding of microglial cells greatly influences Alzheimer’s drug development. Researchers like Beth Stevens focus on how these cells interact within the brain’s immune system, identifying critical pathways that can be targeted to correct malfunctioning processes. This approach leads to innovative drugs aimed at modulating microglial behavior to combat Alzheimer’s symptoms effectively.
What potential advances in Alzheimer’s treatment come from studying synaptic pruning?
Studying synaptic pruning has revealed that it can be both beneficial and detrimental in Alzheimer’s disease. Researching microglial cells that perform pruning allows scientists to identify pathways leading to disease progression, paving the way for treatments that could enhance synaptic health and prevent the cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s.
Why is early detection of Alzheimer’s disease emphasized in current research?
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is emphasized because it allows for timely interventions that may alter the disease’s course. Research initiatives, including those led by Beth Stevens, focus on identifying biomarkers linked to microglial dysfunction, enabling earlier diagnosis and the possibility of implementing preventative strategies before significant cognitive impairment occurs.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Role of Microglia | Microglial cells act as the brain’s immune system, clearing damaged cells and pruning synapses. |
| Aberrant Pruning | Impaired synaptic pruning by microglia can contribute to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s. |
| Research Impact | Findings support the development of new medicines and early detection biomarkers for Alzheimer’s. |
| Future Projections | With the aging U.S. population, Alzheimer’s cases could double by 2050, dramatically increasing healthcare costs. |
| Funding Importance | Federal funding from the NIH has been crucial for advancing research and understanding microglia. |
| Basic Science Value | Basic science research, like studying mouse visual systems, is essential for discovering disease mechanisms. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s research is at a pivotal moment, with groundbreaking discoveries made by scientists like Beth Stevens reshaping our understanding of the disease. Her exploration into the role of microglial cells has highlighted how immune functions in the brain impact neurodegenerative disorders, particularly Alzheimer’s. As research progresses, the potential for developing innovative treatments and early detection methods grows, promising better living conditions for the millions affected by Alzheimer’s. Continued support for basic science is crucial, as it lays the groundwork for future breakthroughs in combating this debilitating illness.