Is sugar addictive? This question sparks considerable debate among nutrition experts and health enthusiasts alike. While several substances, such as alcohol and nicotine, are recognized as addictive, the evidence surrounding sugar addiction reveals complex psychological and physiological responses. Many people experience overwhelming sugar cravings, often linked to the consumption of highly processed foods, which can lead to habitual overeating. Furthermore, understanding the effects of sugar on our health is crucial for those looking to reduce sugar intake and adopt healthier consumption habits.
The concept of sugar cravings has gained traction in discussions about dietary habits and health outcomes. Some researchers argue that excessive consumption of sweeteners might trigger behaviors reminiscent of substance dependence, raising concerns about our relationship with sugar. Although sugar isn’t labeled as addictive in the same way as illicit drugs, its impact on the body can lead to challenging withdrawal-like symptoms when individuals attempt to cut back on their sugary favors. As society increasingly shifts toward healthier lifestyles, examining the consequences of sugar addiction becomes essential in fostering better eating habits and healthy sugar consumption.
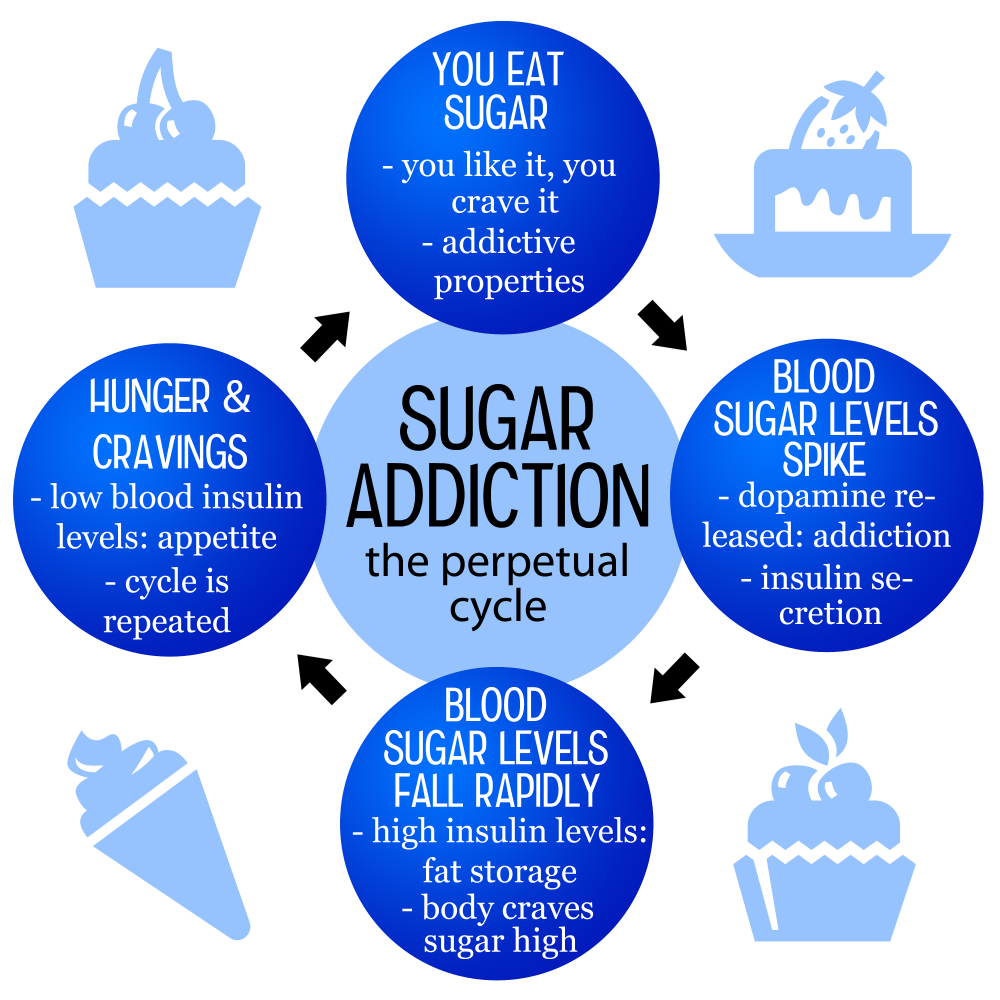
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The debate surrounding sugar addiction is complex. While sugar does elicit cravings and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors, classifying it on par with substances like alcohol or nicotine is contentious. Most experts, including those at Harvard, suggest that while sugar may trigger a physiological response similar to addictive substances, it does not meet the strict medical criteria for addiction. This distinction is crucial; understanding sugar’s addictive qualities can help individuals manage their consumption and cravings effectively.
A normal diet includes sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy, necessary for survival and health. However, excessive added sugar consumption, particularly from ultra-processed foods, can lead to significant health issues. Current estimates suggest that Americans consume almost 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, contributing to obesity and other chronic conditions. Reducing sugar intake is vital for improving health outcomes, emphasizing the importance of moderation rather than complete elimination.
The Effects of Sugar on Your Body
Sugar affects the body in many ways. High sugar consumption has been linked to various health issues such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Notably, when individuals consume too much sugar, it can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. Furthermore, the psychological effects of sugar intake, including mood swings and sugar cravings, can lead individuals to a vicious cycle of consuming more sweetened foods to alleviate these feelings, which in turn exacerbates health problems.
Additionally, sugar impacts brain chemistry, triggering pleasure responses similar to those caused by addictive drugs. This can make it difficult to resist sugary foods, creating cravings that can lead to overconsumption. Educating oneself about the effects of sugar on health is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Exploring healthier sugar consumption strategies, such as incorporating naturally sweet fruits and minimizing processed foods, can lead to better overall well-being.
Strategies to Reduce Sugar Intake
Reducing sugar intake is a gradual process that requires commitment and awareness. One effective strategy is to read food labels diligently. Understanding the amount of added sugars in various products can empower individuals to make healthier choices. For instance, swapping sugary snacks for healthier options like fruits or nuts can significantly decrease daily sugar consumption. Keeping a food diary can also help track intake and identify patterns that lead to sugar cravings.
Another useful approach is to gradually cut back on added sugars rather than going cold turkey. Rapidly eliminating sugar can provoke withdrawal-like symptoms, discouraging long-term success. Instead, individuals can start by reducing the sugar in their coffee or tea and opting for unsweetened beverages. By making small adjustments over time, it becomes easier to enjoy the sweetness of life without the health risks associated with excessive sugar.
Recognizing Sugar Cravings
Sugar cravings can often be mistaken for true hunger, making it essential to differentiate between the two. Many people experience sudden urges for sugary foods due to fluctuating blood sugar levels, which might indicate a its overconsumption. Recognizing these triggers is key to managing cravings effectively. For example, feelings of fatigue or mood dips may signal a need for healthy nutritional choices rather than immediate sugar boosts.
Additionally, emotional factors often play a significant role in sugar cravings. Stress, boredom, or sadness can lead individuals to seek comfort through sugary foods, reinforcing negative eating habits. Developing alternative coping strategies, such as engaging in physical activity or mindfulness practices, can help curb these cravings and foster healthier emotional responses.
Healthy Sugar Consumption
While sugar is often vilified in health discussions, it’s important to recognize that not all sugars are created equal. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and dairy contribute essential nutrients and energy to our diets. Moderation is key; enjoying these foods as part of a balanced diet can offer the sweetness we crave without the health risks associated with excessive added sugars. Being aware of the sources of sugars in one’s diet can facilitate healthier choices.
Incorporating healthy sugar sources can also enhance dietary habits. Fruits offer a wealth of vitamins and fiber, making them a smart choice to satisfy sweet cravings. Similarly, dairy products provide calcium along with lactose, a natural sugar. Maintaining a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps in supporting sustainable energy levels and minimizing unhealthy sugar cravings.
Curbing Sugar Cravings Effectively
To effectively curb sugar cravings, it’s essential to adopt a holistic approach that encompasses both dietary habits and lifestyle changes. Incorporating more protein and fiber-rich foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels and prolong feelings of fullness, which may diminish the intensity of sugar cravings. Regular meals and snacks that balance macronutrients can prevent sudden spikes and drops in blood sugar, ultimately reducing the urge to indulge in sugary snacks.
In addition to dietary adjustments, hydration plays a pivotal role in managing cravings. Often, our bodies can confuse thirst for hunger, leading to unnecessary snacking. Drinking enough water throughout the day can mitigate false hunger cues and help keep cravings at bay. Furthermore, engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to improve overall mood and reduce stress, both of which can contribute to unhealthy eating patterns.
The Role of Ultra-Processed Foods
The prevalence of ultra-processed foods in the modern diet is a significant factor contributing to excessive sugar consumption. These foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, designed to be hyper-palatable and addictive in nature. Understanding the impact of these products is crucial; frequent exposure to such foods can lead to increased sugar cravings, making it challenging to resist unhealthy eating patterns.
Furthermore, the convenience of ultra-processed foods often leads individuals to choose them over whole, nutritional options. Making a conscious effort to reduce the intake of these foods and replace them with whole, unprocessed options can drastically diminish sugar cravings. Cooking at home and preparing meals from scratch can empower individuals to control the ingredients they consume, creating healthier habits while reducing reliance on sugar-laden products.
The Emotional Aspect of Sugar Consumption
Understanding the emotional connection to sugar consumption is vital for addressing cravings. Many people turn to sugar during stressful or challenging times, seeking comfort in sweet foods as a coping mechanism. Acknowledging this emotional tie can help individuals confront the underlying issues and develop healthier coping strategies. Instead of reaching for a sugary snack during stressful moments, seeking alternative activities such as exercise, meditation, or chatting with a friend can provide the same comfort without the sugar.
Moreover, fostering a positive relationship with foods, including those that contain natural sugars, can further mitigate the emotional need to consume sugary treats. By viewing these foods as enjoyable rather than as forbidden, individuals can better manage their sugar intake without falling into a binge cycle. Balancing enjoyment and health awareness in eating can aid in creating a sustainable approach to managing sugar cravings.
Conclusion: Moderation is Key
In conclusion, while sugar does possess certain addictive-like qualities, labeling it as a strictly addictive substance may overshadow the importance of moderation in consumption. Recognizing the effects of sugar on our bodies and minds can empower individuals to make thoughtful dietary choices. Striving for a balanced approach allows room for healthy sugars while minimizing detrimental effects associated with excessive consumption.
Embracing moderation paves the way for maintaining health and well-being. By understanding sugar’s complexities and adopting healthier consumption habits, individuals can enjoy life’s sweetness without compromising their physical and mental health. The key lies not in eliminating sugar entirely but in making informed and conscious choices about sugar consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like drugs or alcohol?
While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like drugs or alcohol. The effects of sugar on the brain may mimic addiction, causing withdrawal-like symptoms for some when they stop consuming it, but these are generally less severe than those associated with true addictive substances.
What are the effects of sugar on the brain?
Sugar affects the brain by releasing dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This process can create feelings of enjoyment and may lead to sugar cravings, making it feel similar to addictive behaviors. However, in moderation, healthy sugar consumption can enhance the taste and texture of foods without severe consequences.
How can I reduce sugar intake if I think I have a sugar addiction?
To reduce sugar intake, consider gradually decreasing the amount of added sugar in your diet instead of going cold turkey. Swap out sugary snacks for healthier options like fruits and nuts, read food labels to identify hidden sugars, and keep your consumption within the recommendations: no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women daily.
What causes sugar cravings and how can I manage them?
Sugar cravings are often triggered by consuming ultra-processed foods that are high in sugar, fat, and salt, which make them very palatable. To manage these cravings, focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods, stay hydrated, and ensure you’re getting enough nutrients. Mindful eating practices can also help in managing and reducing sugar cravings.
What is healthy sugar consumption and how much is too much?
Healthy sugar consumption refers to consuming sugars primarily from natural sources like fruits, vegetables, and dairy. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons per day for men and 6 teaspoons for women. It’s important to be aware of your intake from processed foods, as these can contribute significantly to sugar consumption.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Sugar increases cravings and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors, but it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Ultra-processed foods with added sugar can amplify cravings and make withdrawal (like headaches or anxiety) noticeable when consumption is reduced. |
| We need some sugar in our diets, as it is found in fruits and dairy, but consumption should be moderated to avoid health issues. |
| The American Heart Association recommends limits on added sugar: 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and less for children. |
| Going cold turkey on sugar can backfire; a gradual reduction is advised. |
| Classifying sugar exactly like drugs or alcohol may be counterproductive; it can enhance pleasure when consumed in appropriate amounts. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question sparks an ongoing debate among researchers, including renowned nutrition experts. Although sugar can stimulate cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it doesn’t meet the clinical criteria to be classified as addictive like substances such as alcohol or nicotine. Understanding the nuances of sugar consumption is essential, as moderate amounts can be beneficial, while excessive intake can lead to health issues. Therefore, while sugar may exhibit some addictive qualities, it is crucial to limit added sugar intake to maintain a balanced and healthy lifestyle.