Alzheimer’s early detection is crucial in the fight against this devastating disease, as catching the warning signs before symptoms surface can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Recent research has highlighted the importance of comprehensive olfactory tests, which assess an individual’s ability to identify and remember different smells, potentially serving as an early indicator of cognitive impairment. Utilizing an innovative home testing for Alzheimer’s, these assessments allow older adults to take part in their own diagnosis comfortably and privately. Studies indicate that those with Alzheimer’s may experience diminished olfactory capabilities, linking neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s to a reduced sense of smell. With ongoing advancements in early detection methods, including the smell test for Alzheimer’s, there is renewed hope for intervention long before the onset of memory loss.
The early identification of Alzheimer’s, often referred to as cognitive health screening, is gaining traction in medical communities around the world. By leveraging innovative techniques, such as home-administered scent assessments, researchers are exploring how taste and odor recognition can signal underlying cognitive issues. This proactive approach not only aids in pinpointing individuals at risk of developing Alzheimer’s but also paves the way for timely therapeutic interventions. Furthermore, the exploration of olfactory function, which relates to our sense of smell, is now being viewed as a vital indicator of neurodegenerative disorders beyond Alzheimer’s. As science uncovers the relationship between reduced olfactory sensitivity and cognitive decline, a clearer path emerges for monitoring brain health effectively.
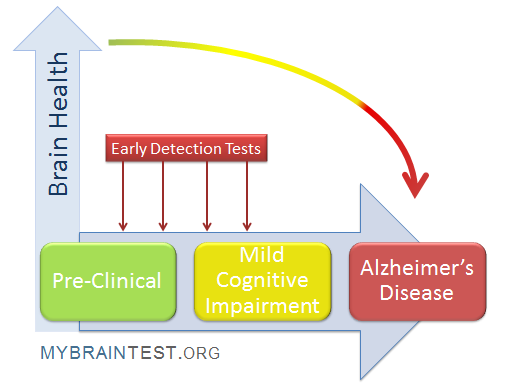
Understanding Alzheimer’s Early Detection
The significance of early detection in Alzheimer’s disease cannot be overstated. Early identification allows for timely interventions that may slow cognitive decline, offering patients and their families a better quality of life. Researchers have been exploring various methods to detect Alzheimer’s before the onset of more severe symptoms. One promising approach involves utilizing olfactory tests, which assess a person’s ability to identify and remember different odors.
These tests have shown that individuals experiencing cognitive impairment often perform poorly on olfactory assessments compared to neurologically healthy peers. The integration of these tests in routine screenings could significantly enhance our ability to detect Alzheimer’s at an earlier stage, enabling targeted preventative measures and tailored therapies that could alter the disease trajectory.
The Role of Olfactory Tests in Alzheimer’s Research
Olfactory tests play a critical role in Alzheimer’s research by providing a non-invasive, cost-effective approach to assessing cognitive function. These tests are designed to measure an individual’s ability to recognize and recall smells, which has been linked to cognitive health. Through large-scale studies, researchers found a correlation between scoring low on these smell tests and higher rates of cognitive decline, highlighting their potential as biomarkers for detecting Alzheimer’s earlier.
Moreover, olfactory dysfunction has been recognized as one of the earliest signs of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s. This connection is particularly relevant as it allows researchers to explore how these tests can be adapted for home use, granting individuals the ability to assess their cognitive health without extensive clinical visits. This innovation could revolutionize the way we approach Alzheimer’s detection across diverse populations.
At-Home Testing for Alzheimer’s: A Game Changer
With advancements in neurocognitive assessments, at-home testing for Alzheimer’s places vital tools right in the hands of consumers. The olfactory test, developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham, enables individuals to assess their cognitive capabilities conveniently within their own homes. This method not only simplifies the detection process but also reduces the stigma often associated with cognitive testing, as users can engage in the evaluation independently.
The practicality of home testing lies in its ability to empower individuals to monitor their health, particularly among older adults or those concerned about cognitive decline. The olfactory test’s accessibility creates an opportunity for early intervention, which is crucial in managing Alzheimer’s disease. As a result, integrating such tests into regular health check-ups could enhance awareness and facilitate discussions about cognitive health among families.
Cognitive Impairment and Olfactory Dysfunction
Cognitive impairment often manifests in subtle ways, making its early detection critical for effective management. Studies indicate a strong link between olfactory dysfunction and cognitive health, with diminished olfactory capabilities serving as a red flag for underlying neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. Identifying this connection has opened new avenues for research into early diagnosis and intervention strategies.
For many individuals, recognizing changes in smell may be one of the first noticeable signs of cognitive impairment. This symptom often precedes more overt memory issues, thus acting as an invaluable early warning system. By focusing on olfactory testing, researchers aim to develop comprehensive screening tools that could capture these early signals, enabling healthcare providers to implement proactive measures against cognitive decline.
Recognizing the Importance of Smell Tests for Alzheimer’s
The smell test for Alzheimer’s disease is not just a novel research tool; it represents a shift towards understanding the multifaceted nature of cognitive decline. Research has shown that those with mild cognitive impairment commonly experience a decrease in their olfactory function, suggesting that integrating these tests into clinical practice could be beneficial. This form of testing is unintrusive and provides real-time feedback on an individual’s cognitive capabilities.
Further research will solidify the role of smell tests within broader diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s. As scientists continue to explore the potential of olfactory dysfunction as an indicator of cognitive health, the tests may become a staple in the early detection process, allowing for timely therapeutic interventions and better health outcomes for individuals at risk.
The Future of Neurodegenerative Disease Assessment
As research progresses, the landscape of neurodegenerative disease assessment is evolving, with olfactory tests at the forefront of innovation. The focus on neuroimaging and cognitive assessments has overshadowed simpler tests like olfactory evaluations; however, recent findings are altering perceptions. The ease of administration and the informative nature of these tests make them a compelling option for initial screenings.
Future studies will likely expand on the findings connecting olfactory decline with Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases, potentially fostering earlier interventions. By validating these tests and broadening their applications, researchers aim to establish a reliable framework for monitoring cognitive health over time, improving the quality of life for those affected by Alzheimer’s disease and their families.
Culturally Inclusive Dementia Testing
One of the significant breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s research has been the recommendation to include culturally inclusive assessments like olfactory tests in diverse populations. Researchers have shown that olfactory function is measurable across different linguistic groups, making it an effective tool for English and Spanish-speaking communities alike. This inclusivity ensures that all individuals have access to cognitive assessments, regardless of their background.
The adaptation of these tests for various cultural contexts is crucial, as it respects the unique perspectives of different populations regarding health and cognitive impairment. By validating olfactory tests in multiple languages, the research team is paving the way for widespread adoption in clinical practice, thereby ensuring equitable access to Alzheimer’s screening and addressing significant health disparities.
Educational Initiatives on Alzheimer’s and Smell Testing
As knowledge of Alzheimer’s disease grows, educational initiatives focusing on the significance of smell testing are becoming increasingly vital. Raising awareness about the early signs of cognitive decline and the role of olfactory function is essential for steering public understanding and encouraging proactive health measures. Such education can empower individuals and families to seek testing sooner, promoting earlier intervention.
Incorporating olfactory tests into educational materials can enhance community understanding of Alzheimer’s symptoms, bolstering acceptance of screening options. These initiatives play a crucial role in shifting perceptions around cognitive health and fostering a culture where proactive assessment is valued and encouraged. As the conversation around Alzheimer’s evolves, equipping individuals with knowledge about smell testing will be paramount.
Advancements in Clinical Research for Alzheimer’s Detection
The rapid advancements in clinical research methodologies continue to enhance the landscape of Alzheimer’s detection. Techniques such as olfactory testing demonstrate how innovative approaches can yield significant insights into neurodegenerative conditions. By integrating these methods into research protocols, scientists are better positioned to track the progression of cognitive decline and correlate it with olfactory performance.
These advancements are not merely academic; they have practical implications for clinical practice and early intervention strategies. As researchers analyze the data derived from olfactory assessments, they will likely reveal vital correlations that could lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. This progress sets the stage for future treatments aimed at mitigating the effects of Alzheimer’s before significant cognitive decline.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Alzheimer’s early detection and why is it important?
Alzheimer’s early detection refers to identifying signs of cognitive impairment before significant memory symptoms arise. Early identification allows for timely interventions and treatment options, potentially slowing disease progression and improving quality of life.
How does an olfactory test relate to Alzheimer’s early detection?
An olfactory test measures a person’s ability to identify and remember odors. Research indicates that olfactory dysfunction can serve as an early warning sign of Alzheimer’s disease, making olfactory testing a valuable tool for Alzheimer’s early detection.
Can I perform home testing for Alzheimer’s using olfactory tests?
Yes! Recent studies have demonstrated that olfactory tests can be conducted at home, allowing individuals to assess their smell abilities safely and conveniently. Home testing for Alzheimer’s can help identify those at risk of cognitive impairment.
What does the smell test for Alzheimer’s involve?
The smell test for Alzheimer’s typically involves sniffing various odor labels on a card and assessing your ability to recognize, discriminate, and remember these smells. Reduced performance on this test may indicate potential cognitive impairment.
How can olfactory dysfunction be used to predict neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s?
Olfactory dysfunction is often one of the earliest signs of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. By evaluating a person’s sense of smell through olfactory tests, researchers and clinicians can better predict the likelihood of developing cognitive impairment.
Are olfactory tests for Alzheimer’s effective across different languages?
Yes, recent studies have shown that olfactory tests for Alzheimer’s can be effectively administered to participants regardless of language. This inclusivity enhances their utility in diverse populations for early detection of cognitive decline.
What types of cognitive impairments can be identified through an olfactory test?
Olfactory tests can help identify various cognitive impairments, particularly those associated with Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment, and other neurodegenerative conditions exhibiting symptoms of smell loss.
Why is it beneficial to detect Alzheimer’s disease early?
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial because it helps facilitate early intervention, better management of symptoms, and access to resources and support, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for those affected.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Research Background | A study by Mass General Brigham reveals that olfactory tests can help detect Alzheimer’s risk. |
| Test Description | Participants sniff odor labels on a card to assess olfactory discrimination, identification, and memory. |
| Target Group | Older adults with subjective cognitive complaints and mild cognitive impairment. |
| Findings | Cognitively impaired older adults performed worse compared to those who were cognitively normal. |
| Future Opportunities | Further studies could validate the test’s efficacy and predict cognitive decline. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s early detection is critical for the timely intervention and management of cognitive decline. Recent research has highlighted a promising olfactory test developed by Mass General Brigham, which allows older adults to assess their risk of Alzheimer’s disease from the comfort of their homes. By identifying the subtle loss of smell as a potential warning sign, this innovative method provides a cost-effective and non-invasive way to promote early diagnosis and future treatment options for Alzheimer’s disease.